Regions
What is a Region?
By now, we have discussed how:
- Root Apps are created
- Creating and registering Apps
- Rendering Root Apps
But we didn't talk about rendering the Child Apps yet.
We do that via Region component, that is shipped with frint-react package.
Illustration
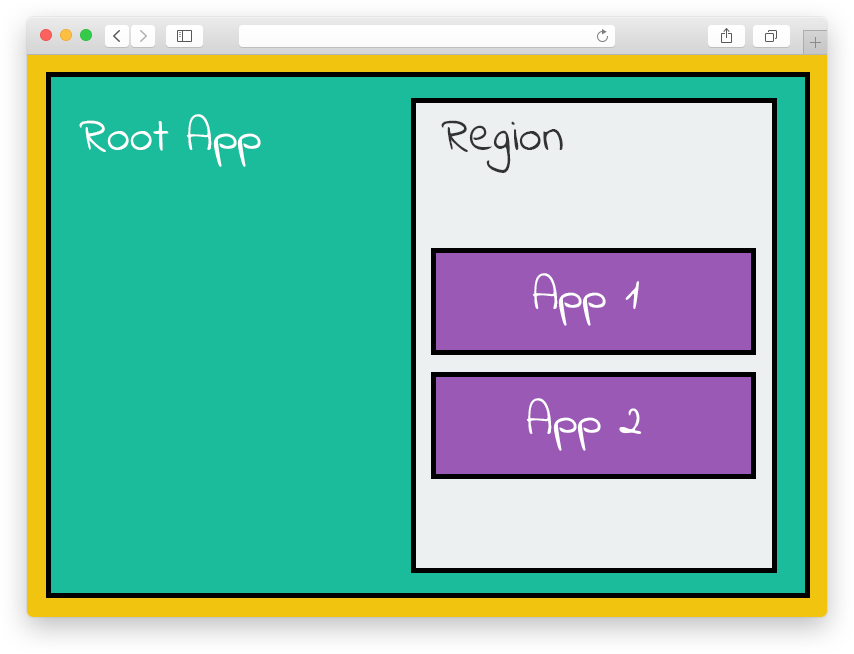
Illustration of a root app, defining a region, where multiple apps get loaded.
We will see some code examples below.
Register Apps with region name
When registering apps, you can pass extra information like the Region where you want it to be mounted on to:
window.app = new App(); // root app
window.app.registerApp(App, {
regions: [
'sidebar'
]
});
We just registered an App in our Root App, and provided enough information to let it know that we want our App to be mounted in a region somewhere which happens to have a name sidebar.
But the sidebar Region does not exist yet. Let's define it next.
Defining a Region
Since Region is a component itself, we can implement it in the root component of our Root App:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Region } from 'frint-react';
class RootComponentOfRootApp extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<section>
<p>Hello world</p>
</section>
<aside>
<Region name="sidebar" />
</aside>
</div>
);
}
}
All we did from our Root App is just to define a Region, and give it a name sidebar.
Now whenever an App becomes available, and it happens to have a target region of the same name, it would get rendered within that specific Region.